Anatomical Models: The Cornerstone of Effective Medical Training
Posted by EMRN on 19th Mar 2024
Anatomical models are indispensable tools in medical education, offering students a tangible and interactive way to explore the complexities of the human body. This blog post delves into the world of anatomical models, highlighting their importance in medical training and the various types available for different educational purposes.
The Importance of Anatomical Models in Medical Training:
- Visualization of Complex Structures: Anatomical models provide a three-dimensional representation of the human body, allowing students to visualize complex structures such as organs, muscles, and bones. This visual aid enhances understanding and retention of anatomical concepts.
- Hands-On Learning Experience: By interacting with anatomical models, students can gain a hands-on learning experience that simulates real-life scenarios. This interactive approach helps students develop a deeper understanding of anatomical relationships and functions.
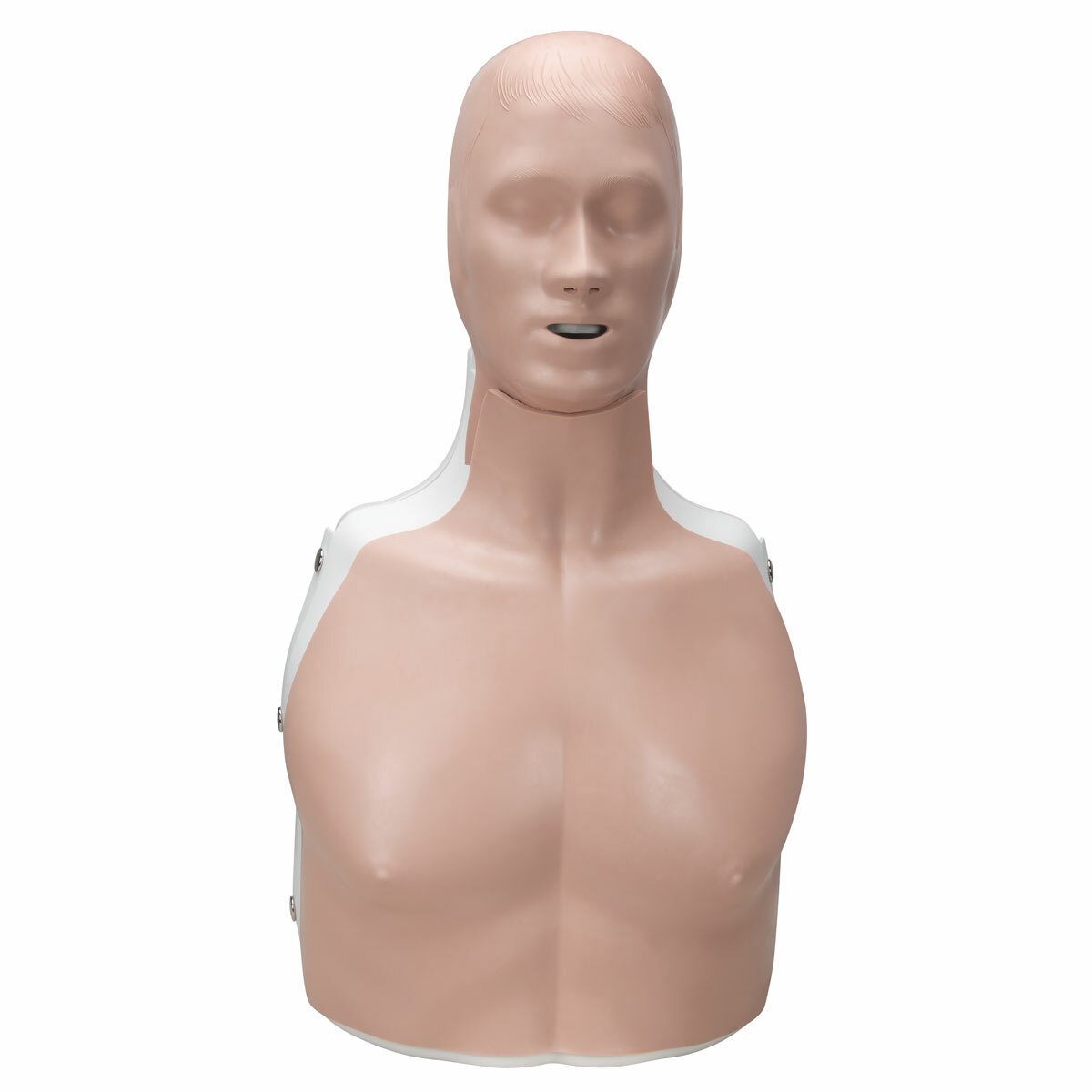
- Clinical Relevance: Anatomical models are designed to mimic the appearance and texture of real human tissues, making them clinically relevant for medical training. This realism allows students to practice procedures and techniques in a safe and controlled environment.
Types of Anatomical Models:
- Human Skeleton Models: Skeleton models are used to study the structure and function of the human skeleton. These models are often articulated to demonstrate joint movements and can be used to teach anatomy, physiology, and biomechanics.
- Organ Models: Organ models replicate the appearance and texture of real human organs. These models are used to study the anatomy and function of specific organs, such as the heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys.
- Muscle Models: Muscle models depict the muscles of the human body, highlighting their origin, insertion, and action. These models are used to teach muscle anatomy and function, as well as techniques such as palpation and muscle testing.
Benefits of Anatomical Models in Medical Training:
- Enhanced Understanding: Anatomical models help students visualize anatomical structures in a way that textbooks and lectures cannot. This visual aid enhances understanding and facilitates the integration of anatomical knowledge into clinical practice.
- Improved Retention: Studies have shown that hands-on learning with anatomical models improves retention of anatomical knowledge. Students who use anatomical models are better able to recall anatomical structures and relationships in clinical settings.
- Skill Development: Anatomical models are valuable tools for developing procedural skills, such as suturing, catheterization, and intubation. By practicing on anatomical models, students can refine their skills and gain confidence in their abilities.
Conclusion:
Anatomical models are essential tools in medical education, offering students a realistic and interactive way to study the complexities of the human body. By providing a hands-on learning experience, anatomical models enhance understanding, retention, and skill development in medical trainees. As medical education continues to evolve, anatomical models will remain a cornerstone of effective and engaging training programs.